+86-0559-5290604
SFP: A Key Component of Future Networks
With the continuous advancement of information technology and the continued growth of network traffic, maintaining efficient network transmission while reducing costs and improving flexibility has become a critical issue for major communications companies. This has led to the emergence of SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable) technology, which has become an indispensable component of modern communications networks.
The Origin and Development of SFP Technology
SFP technology emerged due to the growing demand for fiber-optic communications. Initial network equipment used large optical modules. While these modules offered strong performance, they also presented challenges such as bulk and high cost. With technological advancements, the communications industry's requirements for network modules have continued to rise, demanding not only higher transmission rates but also greater flexibility and scalability. Against this backdrop, SFP technology emerged: a compact module with standardized interfaces that provides fast and stable network transmission.
The SFP module design allows users to replace different fiber modules as needed, achieving compatibility with different fiber standards. This pluggable design not only greatly enhances the flexibility of network equipment but also effectively reduces maintenance costs. The emergence of SFP technology marks the beginning of a modular and flexible era for communications network equipment.

Technical Features and Advantages of SFP Modules
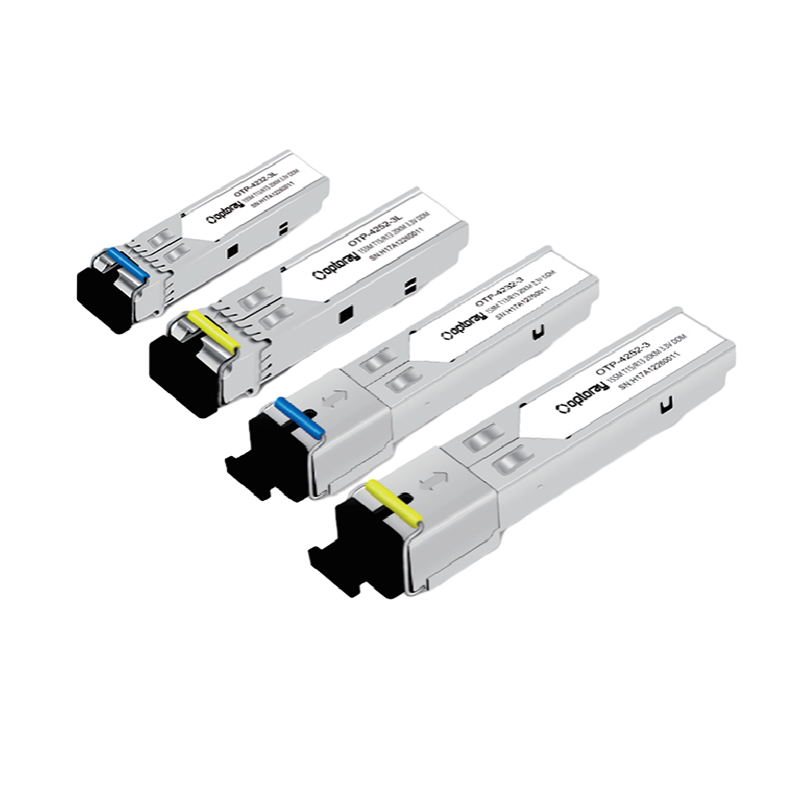
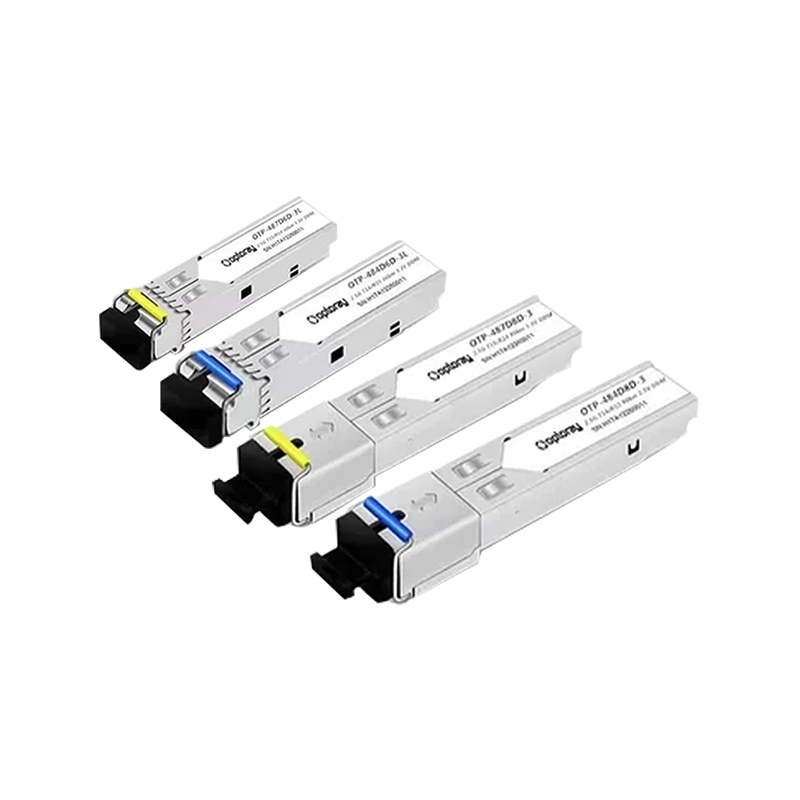
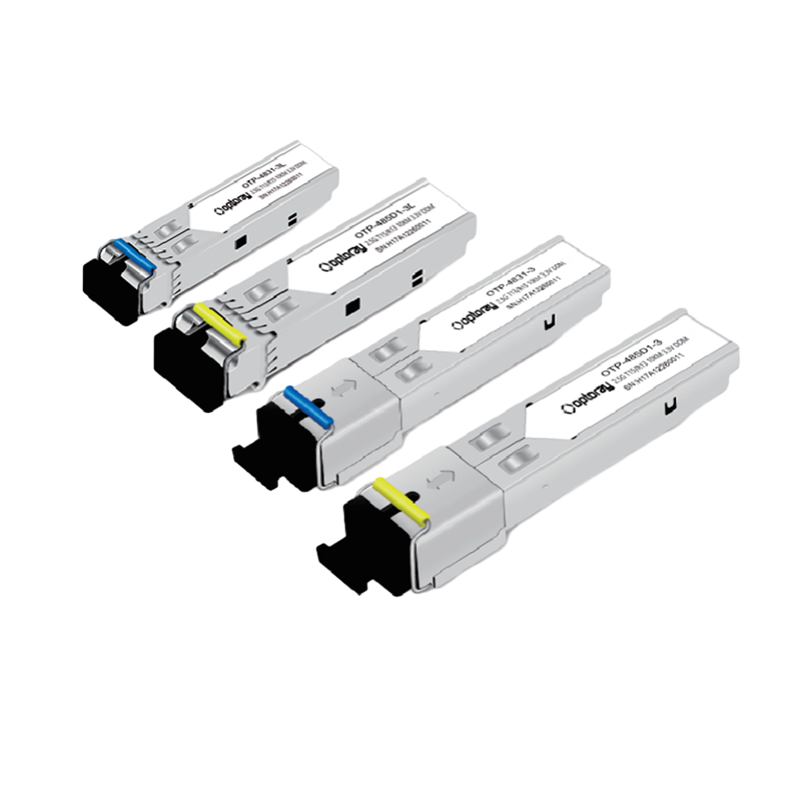
SFP modules utilize a compact design while maintaining high performance, enabling them to fully leverage their advantages in practical applications. SFP modules are highly pluggable, allowing users to replace modules without shutting down the device, significantly improving equipment maintenance efficiency. SFP modules also support hot-swappable technology, meaning they can be replaced while the device is in operation without affecting network connectivity.
SFP modules offer significant advantages in supporting diverse fiber transmission standards. Whether single-mode or multimode fiber, or requiring different transmission distances, users can adapt to their needs by replacing different SFP modules. This flexibility makes SFP modules widely applicable in various network environments.
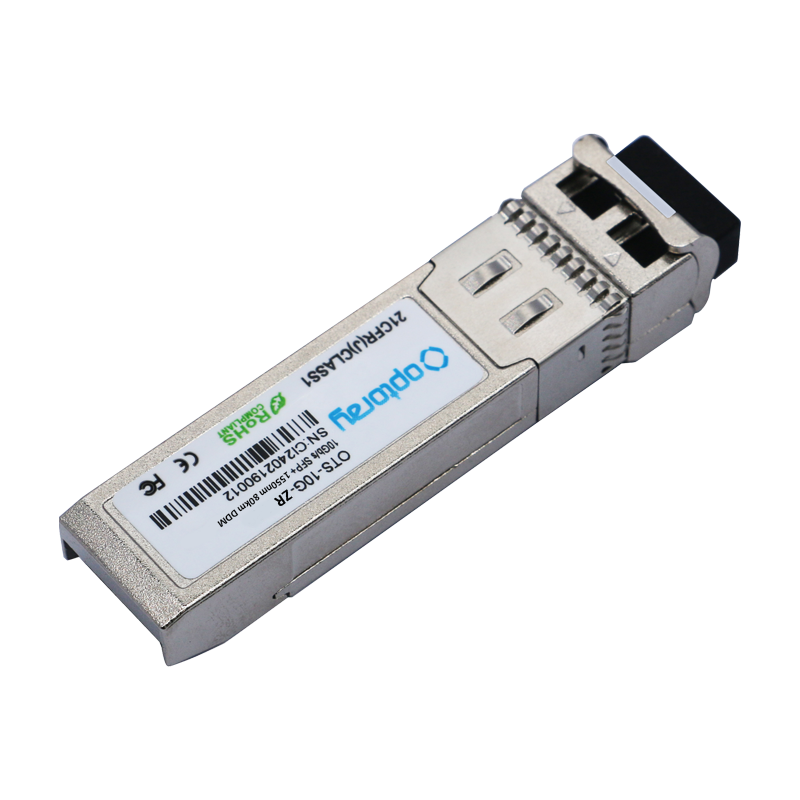
The transmission speed of SFP modules continues to increase. From the initial Gigabit speed to the current 10G, 25G, and even 100G, technological advancements in SFP modules have enabled them to adapt to the ever-changing demands of diverse networks. SFP modules also feature extremely low power consumption, which not only helps reduce energy consumption but also extends the lifespan of equipment.
Comparison of SFP with Other Optical Module Technologies
In the field of fiber optic communications, SFP is not the only option. In addition to SFP modules, there are various other optical module technologies, including QSFP (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable) and XFP (10 Gigabit Small Form-factor Pluggable). Each of these technologies has its own unique advantages, but SFP modules have become one of the most common optical modules in network equipment due to their compact size, low cost, and wide range of transmission rate options.
Compared to QSFP, SFP modules are smaller and suitable for dense equipment designs. Compared to XFP modules, SFP is more cost-competitive and suitable for most enterprise network environments. While other optical modules offer advantages in transmission rate and bandwidth, SFP modules remain the preferred choice for many enterprises due to their flexibility, compatibility, and cost-effectiveness.
Applications of SFP Modules in Modern Communications
In modern networks, SFP modules are widely used, covering data centers, enterprise networks, internet service providers, and the interconnection of various communication devices. In data centers in particular, SFP modules, with their excellent performance and pluggable nature, have become key components for connecting servers, switches, routers, and other devices.

In enterprise networks, SFP modules have even more diverse applications. They can be used not only for building intranets but also for efficient connections to the external internet. Using different types of SFP modules, enterprises can flexibly adjust bandwidth based on network needs, ensuring efficient and stable data transmission.
SFP modules are also widely used in the telecommunications industry and carrier networks. In these environments, SFP modules enable operators to provide high-quality network services and ensure fast data transmission for users.
As a major innovation in the optical module field, SFP technology, with its compact size, high efficiency, and flexibility, plays a vital role in modern communications. From its initial gigabit speeds to today's 10G, 25G, and higher speeds, SFP modules have continued to evolve and meet diverse network needs. With the continuous advancement of network technology, SFP modules will continue to play a vital role in future communication networks, becoming the cornerstone supporting global information transmission.

 English
English русский
русский