+86-0559-5290604
FORGING AHEAD,
LINK FIBER TO FUTURE!
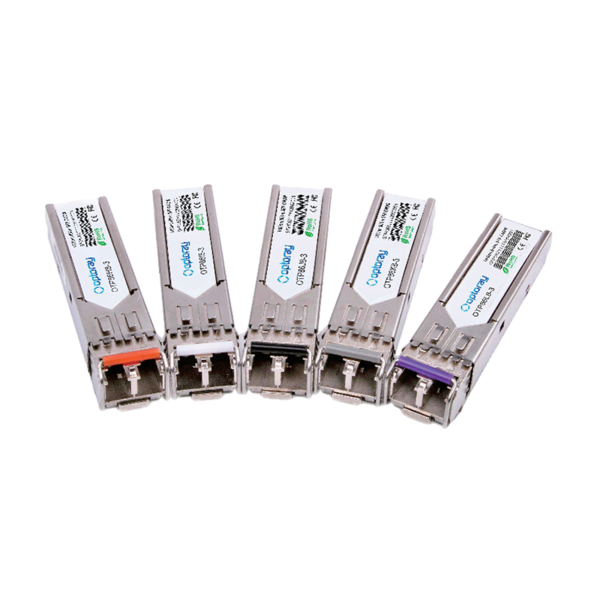
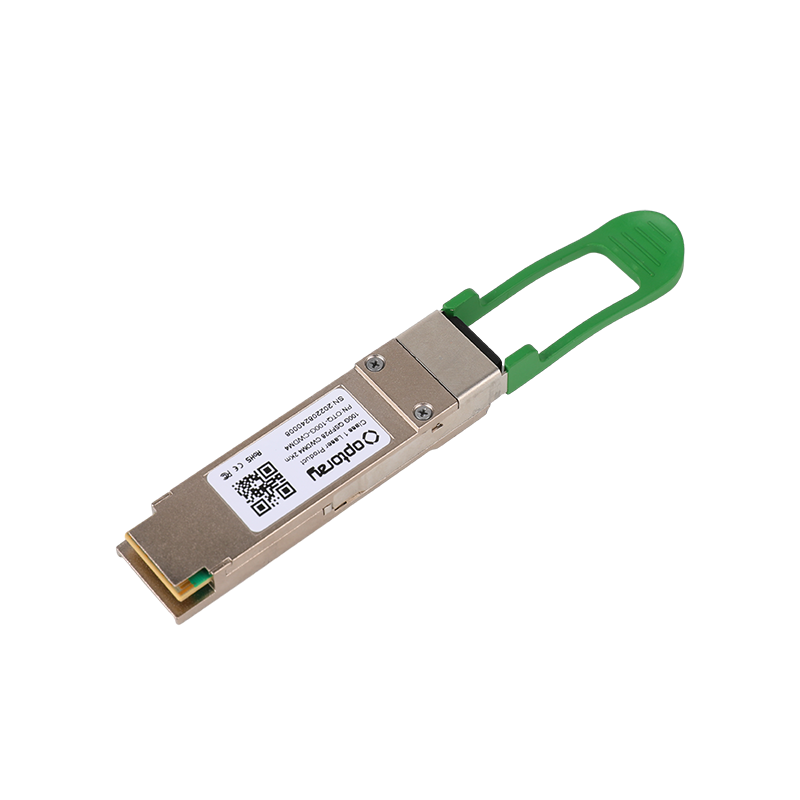
Optoray is China 1.25G CWDM Optical Transceiver Series Manufacturers and 1.25G CWDM Optical Transceiver Series Wholesalers. Optoray has a full series of 1.25G CWDM Optical Transceiver Series and sub-assembly devices from 1Gbps to 400Gbps, which application covers Datacom, Telecom, Video surveillance, and FTTX... And so on. Founded in Huangshan economic development zone, Anhui province in 2007 while the R&D center is in Shenzhen! the phase covers 10,000 square meters. Currently, we already own dozens of related patents and have passed ISO9001:2015 quality system certification and FCC, CE, and RoHS test certification.
Follow company news and information to understand industry trends.
-
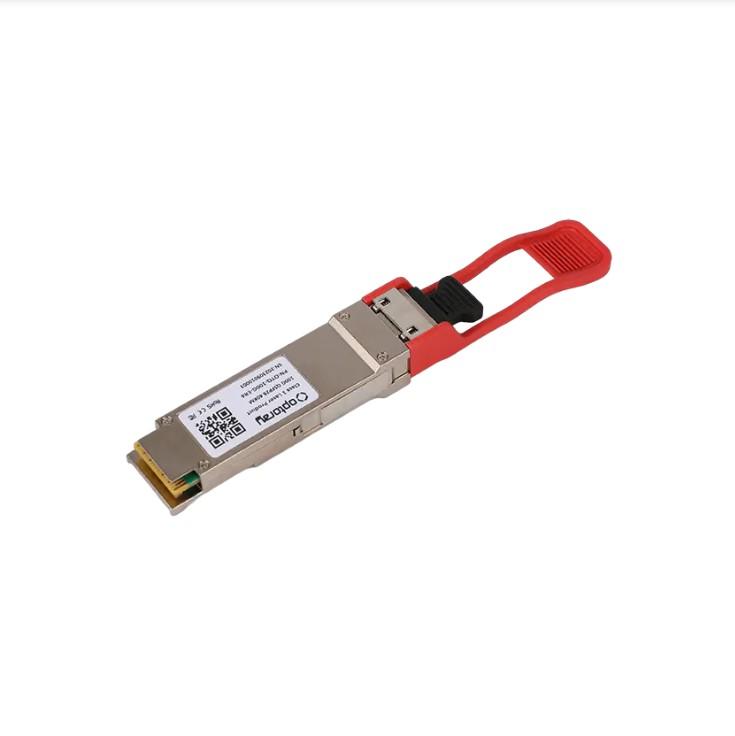 QSFP28-100G-ER4: Is it the ultimate solution for data transmission?
QSFP28-100G-ER4: Is it the ultimate solution for data transmission?In the digital age, the speed and reliability of data transmission are crucial to the development of all walks of life. ...
-
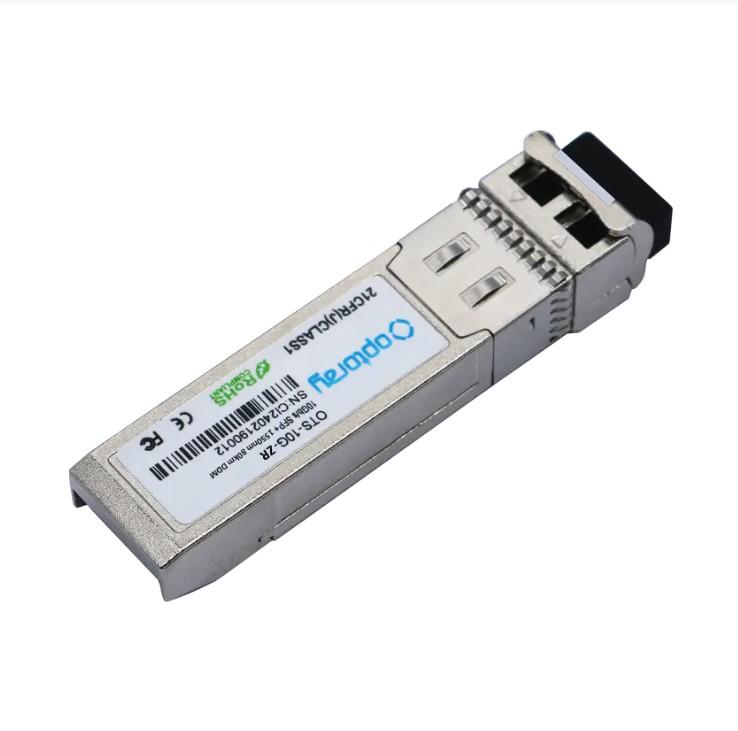 Incredibly innovative! Can 10G SFP duplex modules and 10GBASE-SR multi-mode technology change your understanding of network communications?
Incredibly innovative! Can 10G SFP duplex modules and 10GBASE-SR multi-mode technology change your understanding of network communications?In today's era of digitalization and informationization, the demand for network connections continues to grow, especiall...
-
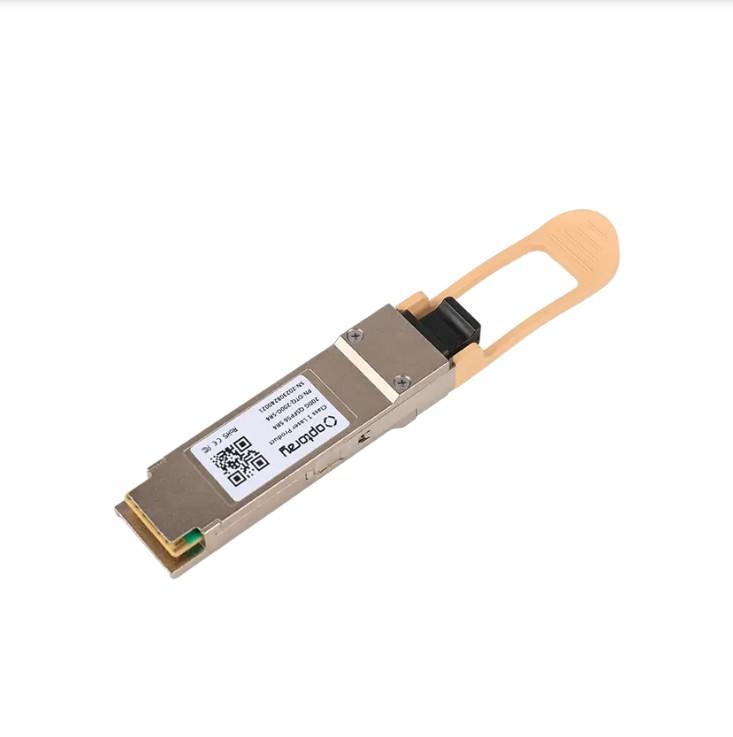 Optical modules: the future of information transmission, are you ready to meet the challenges?
Optical modules: the future of information transmission, are you ready to meet the challenges?With the advent of the digital age, the demand for information transmission speed and capacity is growing day by day. As...
-
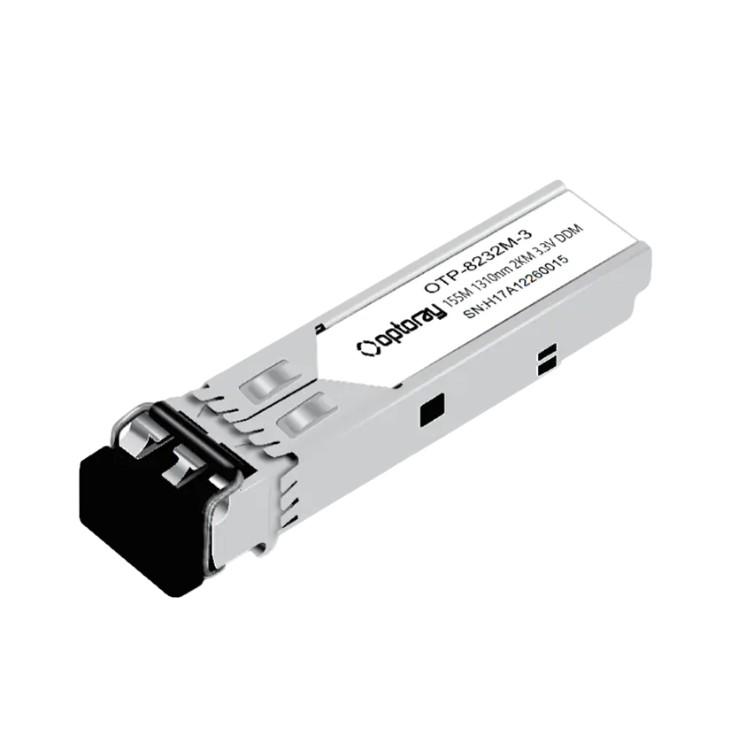 SFP module: critical path to network connectivity?
SFP module: critical path to network connectivity?As a key component of network connection, SFP (Small Form-Factor Pluggable) module is widely used in various fields. Fro...
1.25G CWDM Optical Transceiver Series Industry knowledge
In terms of network security, what encryption and protection measures have been taken for the 1.25G CWDM optical transceiver series?
In terms of network security, the 1.25G CWDM optical transceiver series usually adopts a series of encryption and protection measures to ensure the security and integrity of data transmission. Here are some common encryption and protection measures:
data encryption:
Optical transceivers may support data encryption functions and use encryption algorithms such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) to encrypt transmitted data to prevent data from being illegally intercepted and parsed during transmission.
Authentication and authorization:
Ensure that only authorized devices can access and use optical transceivers by implementing authentication mechanisms such as digital certificates or pre-shared keys.
Access control lists (ACLs) can be used to restrict which devices or users can access specific optical transceiver ports or services.
Physical layer security:
Optical transceiver designs may include physical interface locking mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access and tampering.
Physical characteristics of fiber optic connectors can also be employed to provide additional security, such as specific connector types or interface shapes to reduce the possibility of mismating and unauthorized access.
Security management and monitoring:
Optical transceivers may provide security event logging capabilities to monitor and record potential security events so that potential threats can be discovered and responded to in a timely manner.
Some advanced optical transceivers may also support remote management and monitoring capabilities, allowing network administrators to view the status and security configuration of the device in real time.
Firmware and software updates securely:
Optical transceiver manufacturers typically release firmware and software updates on a regular basis to fix potential security vulnerabilities and enhance security. These updates should be distributed through secure channels and ensure data integrity and security during the update process.
Anti-interference and anti-tampering capabilities:
Considering the particularity of optical signal transmission, optical transceivers may also have anti-interference capabilities to resist electromagnetic interference or other forms of signal interference.
For critical applications, optical transceivers may also need to be tamper-resistant to ensure that hardware and software cannot be illegally modified after deployment.
In a complex network environment, how to ensure the stability and reliability of the 1.25G CWDM optical transceiver series?
In complex network environments, the stability and reliability of the 1.25G CWDM optical transceiver series are crucial. In order to ensure its stable and reliable operation, the following measures are usually taken:
High-Quality Components and Materials:
Use high-quality lasers, photodetectors, filters and other components that are rigorously screened and tested to ensure their performance and reliability.
High-quality materials and processes are used to manufacture the transceiver housing and internal structure to resist environmental interference and physical impact.
Thermal Design and Thermal Management:
In complex network environments, devices may face high temperature and heat dissipation issues. Therefore, optical transceivers adopt reasonable thermal design, including heat sinks, fans, etc., to ensure stable operation under high load and high temperature environments.
At the same time, through precise temperature monitoring and control, damage to optoelectronic devices caused by overheating is avoided.
Electromagnetic compatibility design:
In response to the electromagnetic interference problem in complex network environments, optical transceivers need to be designed for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) to reduce the interference of electromagnetic radiation to other devices and improve their own resistance to electromagnetic interference.
Rigorous testing and verification:
During the production process, optical transceivers need to undergo rigorous testing and verification, including performance testing, environmental adaptability testing, reliability testing, etc., to ensure that they meet design requirements.
Before leaving the factory, an aging test is required to simulate long-term operation to evaluate its long-term stability and reliability.
Software optimization and error handling:
By optimizing software algorithms and logic, the error rate of optical transceivers during data transmission is reduced, and the accuracy and stability of data transmission are improved.
Implement an error detection and recovery mechanism so that when an error occurs, it can automatically correct it or notify the administrator for processing.
Redundancy and backup design:
For critical applications or scenarios with high reliability requirements, optical transceivers may adopt redundant and backup designs, that is, equipped with multiple optical transceiver modules or systems. When one module fails, the backup module can quickly take over the work to ensure the reliability of the network. continuity and stability.

 English
English русский
русский

 +86-186 5596 6697
+86-186 5596 6697