+86-0559-5290604
What is SFP, and What is Its Role in Optical Communication Networks?
In modern optical communication networks, SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable) modules, as high-density, hot-swappable optical transceivers, are gradually becoming indispensable key equipment in data centers, carrier networks, and enterprise networks. Whether for high-speed data transmission or long-distance network coverage, SFP modules provide crucial support for optical network construction with their flexibility, compatibility, and performance advantages.
Technical Principles and Development of SFP Modules
An SFP module is a small, pluggable optical transceiver that converts between optical and electrical signals. Its core principle is to convert electrical signals into optical signals through optoelectronic technology and then transmit them through optical fibers. Because SFPs are hot-swappable, network equipment can have modules replaced or upgraded without shutting down, greatly improving the convenience of network operation and maintenance.
With the development of optical communication technology, SFP modules have evolved from initial low-speed data transmission to supporting various types of high-speed, long-distance, multimode, and single-mode fibers. High-speed SFP modules not only improve the transmission efficiency of internal networks in data centers but also meet the requirements of metropolitan area networks and backbone networks for high bandwidth and high reliability. In addition, the small size of SFP modules allows for high-density port deployment in network equipment, optimizing space utilization and providing more flexibility for network architecture design.
The Key Role of SFP in Network Architecture
In network architecture design, the role of SFP modules is not just a simple data transmission interface. They can select different transmission rates and fiber types according to different network needs, thus achieving flexible network expansion. Whether it's a short-distance local area network or a cross-city backbone network, SFP modules can provide configurable solutions to meet diverse network topology requirements.

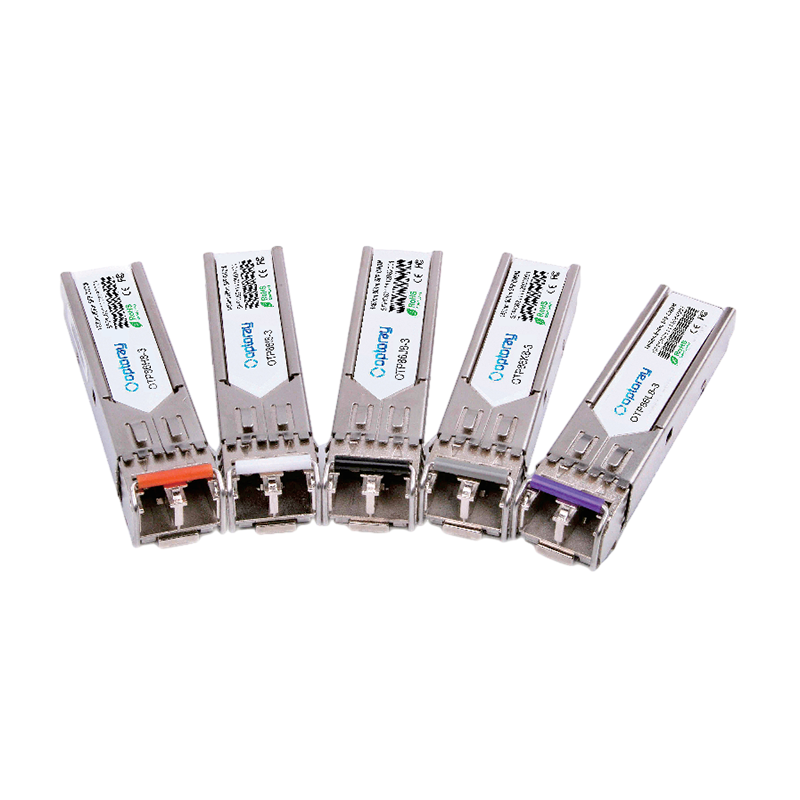
The standardized design of SFP modules makes them compatible with various switches, routers, and optical terminal equipment, enabling interconnection between different brands of equipment. For data centers, this compatibility not only reduces procurement costs but also simplifies network equipment upgrades and maintenance processes. The hot-swappable feature of SFP modules further improves network reliability and reduces the risk of business interruptions caused by equipment maintenance.
Advantages of High-Speed SFP Technology
With the development of emerging technologies such as 5G, cloud computing, and big data, the demands on network bandwidth and latency are constantly increasing. High-speed SFP modules are particularly important in this context. Its main advantages lie in high-speed data transmission, low latency, and high reliability, while also supporting long-distance fiber optic communication, significantly expanding network coverage.
Future Development Trends of SFP Modules
The future development of SFP technology will focus more on high performance, low power consumption, and intelligence. On one hand, with the continuous increase in network demand for high bandwidth, higher speed and higher density SFP modules will become a trend. On the other hand, intelligent SFP modules can achieve remote monitoring and adaptive adjustment, improving network operation and maintenance efficiency and reliability. With the continuous improvement of optical communication standards, SFP modules will play a more central role in future optical network architectures, providing solid support for data center interconnection, metropolitan area network upgrades, and global optical communication development.
At the same time, programmable and modular design concepts will also be widely applied in SFP technology. Through flexible configuration of transmission rate, protocol type, and fiber optic interface type, network operators and enterprises can quickly adjust the network structure according to business needs, reducing overall network construction and maintenance costs. This not only improves network scalability but also enhances the network's ability to cope with sudden traffic demands and technological iterations.
As an important component of optical communication networks, the technological evolution, application value, and future trends of SFP modules are worth in-depth study. By continuously improving performance and intelligence, SFP modules can not only meet the needs of current high-speed networks but also provide a solid foundation for the development of future optical communication technologies. In the network construction of data centers, enterprise networks, and communication operators, SFP modules are undoubtedly indispensable core components.
FAQ
What is the difference between SFP and SFP+ modules?
SFP+ is an upgraded version of SFP, supporting higher transmission rates and is usually used in high-speed data centers and long-distance fiber optic networks.
Can SFP modules be replaced freely?
SFP modules support hot-swapping, but compatibility and device support must be ensured to avoid instability or incompatibility issues.
What is the typical lifespan of an SFP module?
The lifespan of an SFP module depends on the working environment and usage frequency, usually reaching tens of thousands of hours, but long-term high temperature or high power consumption will affect its lifespan.
How to choose a suitable SFP module?
Choosing an SFP module requires comprehensive consideration of factors such as transmission rate, fiber type, transmission distance, and device compatibility to ensure that it meets network construction needs.

 English
English русский
русский